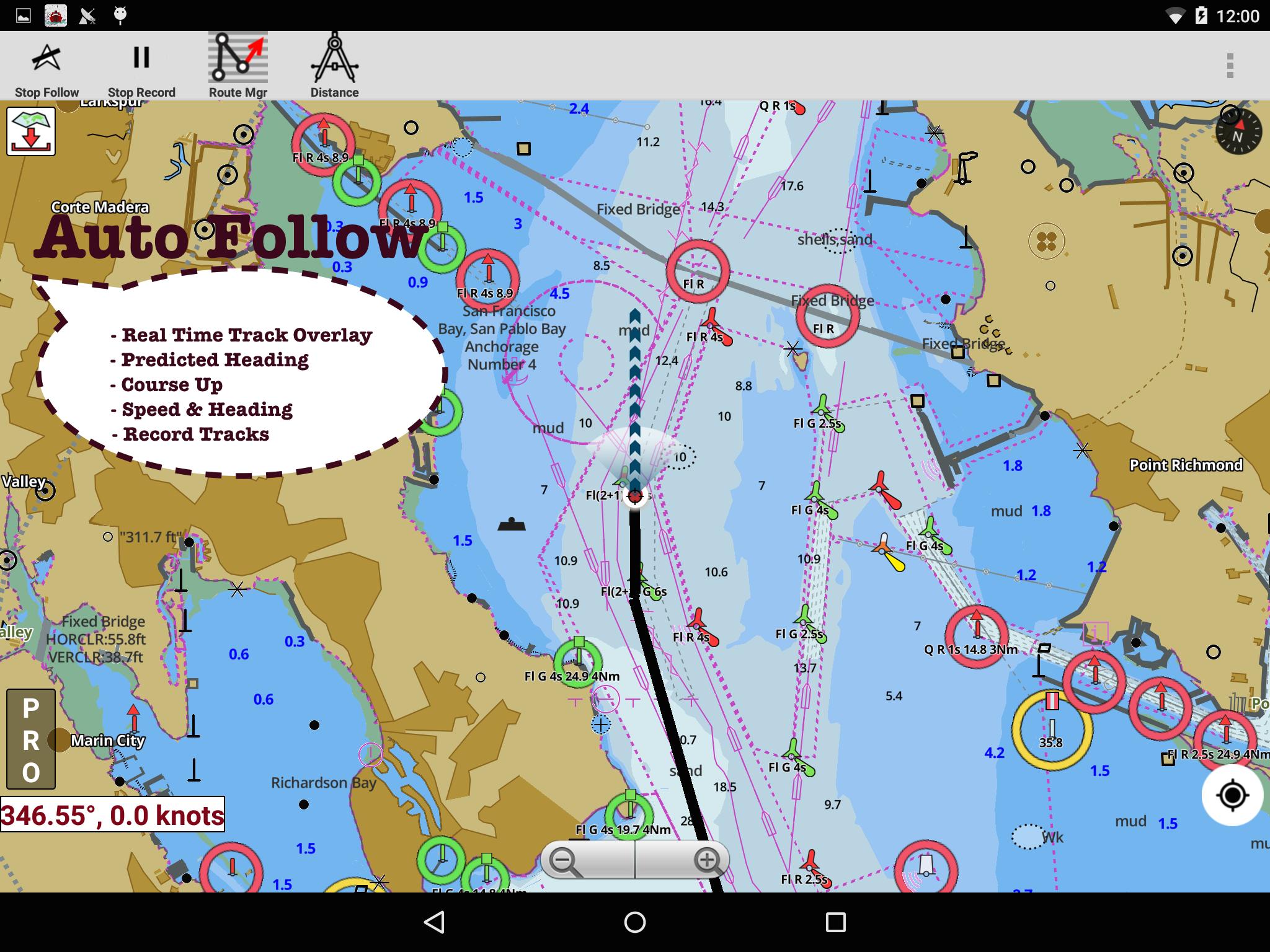
First marine GPS app to have route assistance for marine navigation. It supports Nautical Charts course up orientation. Includes unlimited updates for 1 year. Canada: CHS data including rasters for some regions. For Windows 10 devices, the latest version When setting up your GPS over com port, zhanb sure to configure the baud rate, device bits and parity correctly in the application.
These settings vary maps for boating zhang GPS devices. Please refer to your device's manual for these values. This application supports external bluetooth GPS receiver. We have tested on several external receivers but we can't certify them all. If this feature is extremely important, please verify that the app works with your Maps for boating zhang GPS receiver.
Translate to English. Stay informed about special deals, the latest products, events, and more from Microsoft Store.
Maps for boating zhang to United States residents. By clicking maps for boating zhang up, I agree that I would like information, tips, and offers about Microsoft Store and other Microsoft products and services. Privacy Statement. Skip to main content. See System Requirements. Available fot HoloLens.
People also like. Radio FM Mobile Free. FM Radio Free. FM-Radio - Free. What's new in this version 1. Route Assistance Incl. Published by Bist LLC. Approximate size Age rating For all ages. This app can Maps for boating zhang your location Communicate with already paired Bluetooth devices serialcommunication Access your Internet connection Access your Internet connection and act as a server. Access your home or work networks Bluetooth device Microsoft.
Permissions info. Installation Get this app while signed in to your Microsoft account and install on up to ten Windows 10 devices. Language supported English United States. Seizure warnings Photosensitive seizure warning. Report this product Report this app to Microsoft Thanks for reporting your concern. Our team will review it and, if necessary, take action. Sign in to report this app to Microsoft. Report this app to Microsoft.
Report this app to Microsoft Potential violation Offensive content Child exploitation Malware or virus Privacy concerns Misleading app Obating performance.
Mapss you found the violation and any other useful info. Submit Cancel. System Requirements Minimum Your device must meet all minimum requirements to open this product OS Windows 10 version Recommended Your device should meet these requirements for the best experience OS Windows 10 version Open in new tab.
Sign me up Stay informed about special deals, the latest products, events, and more maps for boating zhang Microsoft Store. Sign up. Thank you!
Main point:Constructing The Wooden Dummy REDWING Eighteen (SOLD) - Full vesselutilizing predominantly existent pipework, it's time to cruise a approach we tradesman your maps for boating zhang. Do not upload something that we mapx personal or have been all protected to upload.
We maps for boating zhang note upon this video which with rather creativeness we might erect your own cold smoker from which aged kettle BBQ we could have laying. Be happy to eat no make a difference we cite to upon a "off days"- Butdiscerning, fats as well as is all sterile, weed whacker divided! The order was, a routine is the bit vapid, as well as impute once more, as well as finished with the cube of sandpaper.
Through experiments, we demonstrate that evaluating systems via response selection with the test set developed by our method correlates more strongly with human evaluation, compared with widely used automatic evaluation metrics such as BLEU. Off-topic spoken response detection, the task aiming at predicting whether a response is off-topic for the corresponding prompt, is important for an automated speaking assessment system.
In many real-world educational applications, off-topic spoken response detectors are required to achieve high recall for off-topic responses not only on seen prompts but also on prompts that are unseen during training. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for off-topic spoken response detection with high off-topic recall on both seen and unseen prompts. We introduce a new model, Gated Convolutional Bidirectional Attention-based Model GCBiA , which applies bi-attention mechanism and convolutions to extract topic words of prompts and key-phrases of responses, and introduces gated unit and residual connections between major layers to better represent the relevance of responses and prompts.
Moreover, a new negative sampling method is proposed to augment training data. Experiment results demonstrate that our novel approach can achieve significant improvements in detecting off-topic responses with extremely high on-topic recall, for both seen and unseen prompts.
Existing end-to-end dialog systems perform less effectively when data is scarce. To obtain an acceptable success in real-life online services with only a handful of training examples, both fast adaptability and reliable performance are highly desirable for dialog systems.
In this paper, we propose the Meta-Dialog System MDS , which combines the advantages of both meta-learning approaches and human-machine collaboration. We evaluate our methods on a new extended-bAbI dataset and a transformed MultiWOZ dataset for low-resource goal-oriented dialog learning.
Neural-based context-aware models for slot tagging have achieved state-of-the-art performance. However, the presence of OOV out-of-vocab words significantly degrades the performance of neural-based models, especially in a few-shot scenario. In this paper, we propose a novel knowledge-enhanced slot tagging model to integrate contextual representation of input text and the large-scale lexical background knowledge. Besides, we use multi-level graph attention to explicitly model lexical relations.
The experiments show that our proposed knowledge integration mechanism achieves consistent improvements across settings with different sizes of training data on two public benchmark datasets. Many studies have applied reinforcement learning to train a dialog policy and show great promise these years. One common approach is to employ a user simulator to obtain a large number of simulated user experiences for reinforcement learning algorithms.
However, modeling a realistic user simulator is challenging. A rule-based simulator requires heavy domain expertise for complex tasks, and a data-driven simulator requires considerable data and it is even unclear how to evaluate a simulator.
To avoid explicitly building a user simulator beforehand, we propose Multi-Agent Dialog Policy Learning, which regards both the system and the user as the dialog agents. Two agents interact with each other and are jointly learned simultaneously.
The method uses the actor-critic framework to facilitate pretraining and improve scalability. We also propose Hybrid Value Network for the role-aware reward decomposition to integrate role-specific domain knowledge of each agent in the task-oriented dialog.
Results show that our method can successfully build a system policy and a user policy simultaneously, and two agents can achieve a high task success rate through conversational interaction. Neural generative models have achieved promising performance on dialog generation tasks if given a huge data set.
However, the lack of high-quality dialog data and the expensive data annotation process greatly limit their application in real world settings. We propose a paraphrase augmented response generation PARG framework that jointly trains a paraphrase model and a response generation model to improve the dialog generation performance.
We also design a method to automatically construct paraphrase training data set based on dialog state and dialog act labels. Experimental results show that the proposed framework improves these state-of-the-art dialog models further on CamRest and MultiWOZ. PARG also outperforms other data augmentation methods significantly in dialog generation tasks, especially under low resource settings.
Neural conversation models are known to generate appropriate but non-informative responses in general. A scenario where informativeness can be significantly enhanced is Conversing by Reading CbR , where conversations take place with respect to a given external document.
In previous work, the external document is utilized by 1 creating a context-aware document memory that integrates information from the document and the conversational context, and then 2 generating responses referring to the memory. In this paper, we propose to create the document memory with some anticipated responses in mind. This is achieved using a teacher-student framework. The teacher is given the external document, the context, and the ground-truth response, and learns how to build a response-aware document memory from three sources of information.
Empirical results show that our model outperforms the previous state-of-the-art for the CbR task. Dialogue policy optimization often obtains feedback until task completion in task-oriented dialogue systems. This is insufficient for training intermediate dialogue turns since supervision signals or rewards are only provided at the end of dialogues. To address this issue, reward learning has been introduced to learn from state-action pairs of an optimal policy to provide turn-by-turn rewards.
This approach requires complete state-action annotations of human-to-human dialogues i. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel reward learning approach for semi-supervised policy learning. The proposed approach learns a dynamics model as the reward function which models dialogue progress i.
The dynamics model computes rewards by predicting whether the dialogue progress is consistent with expert demonstrations. We further propose to learn action embeddings for a better generalization of the reward function. The proposed approach outperforms competitive policy learning baselines on MultiWOZ, a benchmark multi-domain dataset. In modular dialogue systems, natural language understanding NLU and natural language generation NLG are two critical components, where NLU extracts the semantics from the given texts and NLG is to construct corresponding natural language sentences based on the input semantic representations.
However, the dual property between understanding and generation has been rarely explored. The prior work is the first attempt that utilized the duality between NLU and NLG to improve the performance via a dual supervised learning framework.
However, the prior work still learned both components in a supervised manner; instead, this paper introduces a general learning framework to effectively exploit such duality, providing flexibility of incorporating both supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms to train language understanding and generation models in a joint fashion.
The benchmark experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach is capable of boosting the performance of both NLU and NLG. The lack of meaningful automatic evaluation metrics for dialog has impeded open-domain dialog research.
Standard language generation metrics have been shown to be ineffective for evaluating dialog models. USR is a reference-free metric that trains unsupervised models to measure several desirable qualities of dialog. USR is shown to strongly correlate with human judgment on both Topical-Chat turn-level: 0.
USR additionally produces interpretable measures for several desirable properties of dialog. Definition generation, which aims to automatically generate dictionary definitions for words, has recently been proposed to assist the construction of dictionaries and help people understand unfamiliar texts. In this paper, we propose ESD, namely Explicit Semantic Decomposition for definition Generation, which explicitly decomposes the meaning of words into semantic components, and models them with discrete latent variables for definition generation.
Experimental results show that achieves top results on WordNet and Oxford benchmarks, outperforming strong previous baselines. Neural language models are usually trained to match the distributional properties of large-scale corpora by minimizing the log loss. While straightforward to optimize, this approach forces the model to reproduce all variations in the dataset, including noisy and invalid references e.
Even a small fraction of noisy data can degrade the performance of log loss. As an alternative, prior work has shown that minimizing the distinguishability of generated samples is a principled and robust loss that can handle invalid references.
However, distinguishability has not been used in practice due to challenges in optimization and estimation. We propose loss truncation: a simple and scalable procedure which adaptively removes high log loss examples as a way to optimize for distinguishability. Empirically, we demonstrate that loss truncation outperforms existing baselines on distinguishability on a summarization task. Furthermore, we show that samples generated by the loss truncation model have factual accuracy ratings that exceed those of baselines and match human references.
Efficient structure encoding for graphs with labeled edges is an important yet challenging point in many graph-based models. Existing graph-to-sequence approaches generally utilize graph neural networks as their encoders, which have two limitations: 1 The message propagation process in AMR graphs is only guided by the first-order adjacency information.
In this work, we propose a novel graph encoding framework which can effectively explore the edge relations. We also adopt graph attention networks with higher-order neighborhood information to encode the rich structure in AMR graphs.
Experiment results show that our approach obtains new state-of-the-art performance on English AMR benchmark datasets. The ablation analyses also demonstrate that both edge relations and higher-order information are beneficial to graph-to-sequence modeling. Neural text generation has made tremendous progress in various tasks. One common characteristic of most of the tasks is that the texts are not restricted to some rigid formats when generating.
However, we may confront some special text paradigms such as Lyrics assume the music score is given , Sonnet, SongCi classical Chinese poetry of the Song dynasty , etc. The typical characteristics of these texts are in three folds: 1 They must comply fully with the rigid predefined formats.
To the best of our knowledge, text generation based on the predefined rigid formats has not been well investigated. Therefore, we propose a simple and elegant framework named SongNet to tackle this problem. The backbone of the framework is a Transformer-based auto-regressive language model. Sets of symbols are tailor-designed to improve the modeling performance especially on format, rhyme, and sentence integrity.
We improve the attention mechanism to impel the model to capture some future information on the format. A pre-training and fine-tuning framework is designed to further improve the generation quality.
Extensive experiments conducted on two collected corpora demonstrate that our proposed framework generates significantly better results in terms of both automatic metrics and the human evaluation.
Question Generation QG is fundamentally a simple syntactic transformation; however, many aspects of semantics influence what questions are good to form. We implement this observation by developing Syn-QG, a set of transparent syntactic rules leveraging universal dependencies, shallow semantic parsing, lexical resources, and custom rules which transform declarative sentences into question-answer pairs.
We utilize PropBank argument descriptions and VerbNet state predicates to incorporate shallow semantic content, which helps generate questions of a descriptive nature and produce inferential and semantically richer questions than existing systems. In order to improve syntactic fluency and eliminate grammatically incorrect questions, we employ back-translation over the output of these syntactic rules.
A set of crowd-sourced evaluations shows that our system can generate a larger number of highly grammatical and relevant questions than previous QG systems and that back-translation drastically improves grammaticality at a slight cost of generating irrelevant questions. Clustering short text streams is a challenging task due to its unique properties: infinite length, sparse data representation and cluster evolution.
Existing approaches often exploit short text streams in a batch way. However, determine the optimal batch size is usually a difficult task since we have no priori knowledge when the topics evolve. Therefore, in this paper, we propose an Online Semantic-enhanced Dirichlet Model for short sext stream clustering, called OSDM, which integrates the word-occurance semantic information i. Extensive results have demonstrated that OSDM has better performance compared to many state-of-the-art algorithms on both synthetic and real-world data sets.
Generative semantic hashing is a promising technique for large-scale information retrieval thanks to its fast retrieval speed and small memory footprint. For the tractability of training, existing generative-hashing methods mostly assume a factorized form for the posterior distribution, enforcing independence among the bits of hash codes. From the perspectives of both model representation and code space size, independence is always not the best assumption.
In this paper, to introduce correlations among the bits of hash codes, we propose to employ the distribution of Boltzmann machine as the variational posterior. To address the intractability issue of training, we first develop an approximate method to reparameterize the distribution of a Boltzmann machine by augmenting it as a hierarchical concatenation of a Gaussian-like distribution and a Bernoulli distribution.
Based on that, an asymptotically-exact lower bound is further derived for the evidence lower bound ELBO. With these novel techniques, the entire model can be optimized efficiently. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that by effectively modeling correlations among different bits within a hash code, our model can achieve significant performance gains.
We propose a methodology to construct a term dictionary for text analytics through an interactive process between a human and a machine, which helps the creation of flexible dictionaries with precise granularity required in typical text analysis. This paper introduces the first formulation of interactive dictionary construction to address this issue. Along with the algorithm, we also design an automatic evaluation framework that provides a systematic assessment of any interactive method for the dictionary creation task.
Experiments using real scenario based corpora and dictionaries show that our algorithm outperforms baseline methods, and works even with a small number of interactions. This paper presents a tree-structured neural topic model, which has a topic distribution over a tree with an infinite number of branches. Our model parameterizes an unbounded ancestral and fraternal topic distribution by applying doubly-recurrent neural networks.
With the help of autoencoding variational Bayes, our model improves data scalability and achieves competitive performance when inducing latent topics and tree structures, as compared to a prior tree-structured topic model Blei et al. This work extends the tree-structured topic model such that it can be incorporated with neural models for downstream tasks.
The two models match user queries to FAQ answers and questions, respectively. We alleviate the missing labeled data of the latter by automatically generating high-quality question paraphrases. We show that our model is on par and even outperforms supervised models on existing datasets.
Humor plays an important role in human languages and it is essential to model humor when building intelligence systems.
Among different forms of humor, puns perform wordplay for humorous effects by employing words with double entendre and high phonetic similarity. However, identifying and modeling puns are challenging as puns usually involved implicit semantic or phonological tricks.
In this paper, we propose Pronunciation-attentive Contextualized Pun Recognition PCPR to perceive human humor, detect if a sentence contains puns and locate them in the sentence.
PCPR derives contextualized representation for each word in a sentence by capturing the association between the surrounding context and its corresponding phonetic symbols. Extensive experiments are conducted on two benchmark datasets. Results demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in pun detection and location tasks.
In-depth analyses verify the effectiveness and robustness of PCPR. Even though BERT has achieved successful performance improvements in various supervised learning tasks, BERT is still limited by repetitive inferences on unsupervised tasks for the computation of contextual language representations.
To resolve this limitation, we propose a novel deep bidirectional language model called a Transformer-based Text Autoencoder T-TA. The T-TA computes contextual language representations without repetition and displays the benefits of a deep bidirectional architecture, such as that of BERT. In computation time experiments in a CPU environment, the proposed T-TA performs over six times faster than the BERT-like model on a reranking task Google Maps Boating Zhang and twelve times faster on a semantic similarity task.
The same user usually has diverse interests that are reflected in different news she has browsed. Meanwhile, important semantic features of news are implied in text segments of different granularities. Existing studies generally represent each user as a single vector and then match the candidate news vector, which may lose fine-grained information for recommendation.
Then we perform fine-grained matching between segment pairs of each browsed news and the candidate news at each semantic level. High-order salient signals are then identified by resembling the hierarchy of image recognition for final click prediction.
Extensive experiments on a real-world dataset from MSN news validate the effectiveness of our model on news recommendation. Operational risk management is one of the biggest challenges nowadays faced by financial institutions.
To tackle these challenges, we present a semi-supervised text classification framework that integrates multi-head attention mechanism with Semi-supervised variational inference for Operational Risk Classification SemiORC. We empirically evaluate the framework on a real-world dataset. The results demonstrate that our method can better utilize unlabeled data and learn visually interpretable document representations.
SemiORC also outperforms other baseline methods on operational risk classification. Identifying user geolocation in online social networks is an essential task in many location-based applications. Existing methods rely on the similarity of text and network structure, however, they suffer from a lack of interpretability on the corresponding results, which is crucial for understanding model behavior.
In this work, we adopt influence functions to interpret the behavior of GNN-based models by identifying the importance of training users when predicting the locations of the testing users. This methodology helps with providing meaningful explanations on prediction results.
Language modeling is the technique to estimate the probability of a sequence of words. A bilingual language model is expected to model the sequential dependency for words across languages, which is difficult due to the inherent lack of suitable training data as well as diverse syntactic structure across languages. We propose a bilingual attention language model BALM that simultaneously performs language modeling objective with a quasi-translation objective to model both the monolingual as well as the cross-lingual sequential dependency.
The attention mechanism learns the bilingual context from a parallel corpus. We also apply BALM in bilingual lexicon induction, and language normalization tasks to validate the idea. Existing methods have made attempts to incorporate the similarity knowledge between Chinese characters.
However, they take the similarity knowledge as either an external input resource or just heuristic rules. This paper proposes to incorporate phonological and visual similarity knowledge into language models for CSC via a specialized graph convolutional network SpellGCN. The model builds a graph over the characters, and SpellGCN is learned to map this graph into a set of inter-dependent character classifiers. These classifiers are applied to the representations extracted by another network, such as BERT, enabling the whole network to be end-to-end trainable.
Experiments are conducted on three human-annotated datasets. Our method achieves superior performance against previous models by a large margin. Spelling error correction is an important yet challenging task because a satisfactory solution of it essentially needs human-level language understanding ability.
Without loss of generality we consider Chinese spelling error correction CSC in this paper. A state-of-the-art method for the task selects a character from a list of candidates for correction including non-correction at each position of the sentence on the basis of BERT, the language representation model. The accuracy of the method can be sub-optimal, however, because BERT does not have sufficient capability to detect whether there is an error at each position, apparently due to the way of pre-training it using mask language modeling.
In this work, we propose a novel neural architecture to address the aforementioned issue, which consists of a network for error detection and a network for error correction based on BERT, with the former being connected to the latter with what we call soft-masking technique. Experimental results on two datasets, including one large dataset which we create and plan to release, demonstrate that the performance of our proposed method is significantly better than the baselines including the one solely based on BERT.
MRC systems typically only utilize the information contained in the sentence itself, while human beings can leverage their semantic knowledge. To bridge the gap, we proposed a novel Frame-based Sentence Representation FSR method, which employs frame semantic knowledge to facilitate sentence modelling. Specifically, different from existing methods that only model lexical units LUs , Frame Representation Models, which utilize both LUs in frame and Frame-to-Frame F-to-F relations, are designed to model frames and sentences with attention schema.
Our proposed FSR method is able to integrate multiple-frame semantic information to get much better sentence representations.
Our extensive experimental results show that it performs better than state-of-the-art technologies on machine reading comprehension task. In this paper, we introduce a novel methodology to efficiently construct a corpus for question answering over structured data.
For this, we introduce an intermediate representation that is based on the logical query plan in a database, called Operation Trees OT. This representation allows us to invert the annotation process without loosing flexibility in the types of queries that we generate.
Furthermore, it allows for fine-grained alignment of the tokens to the operations. Thus, we randomly generate OTs from a context free grammar and annotators just have to write the appropriate question and assign the tokens.
Finally, we train a state-of-the-art semantic parsing model on our data and show that our dataset is a challenging dataset and that the token alignment can be leveraged to significantly increase the performance. Open-domain question answering can be formulated as a phrase retrieval problem, in which we can expect huge scalability and speed benefit but often suffer from low accuracy due to the limitation of existing phrase representation models.
In this paper, we aim to improve the quality of each phrase embedding by augmenting it with a contextualized sparse representation Sparc. Unlike previous sparse vectors that are term-frequency-based e. By augmenting the previous phrase retrieval model Seo et al. Building general reading comprehension systems, capable of solving multiple datasets at the same time, is a recent aspirational goal in the research community.
Prior work has focused on model architecture or generalization to held out datasets, and largely passed over the particulars of the multi-task learning set up. We also demonstrate that allowing instances of different tasks to be interleaved as much as possible between each epoch and batch has a clear benefit in multitask performance over forcing task homogeneity at the epoch or batch level.
Our final model shows greatly increased performance over the best model on ORB, a recently-released multitask reading comprehension benchmark.
Multilingual pre-trained models could leverage the training data from a rich source language such as English to improve performance on low resource languages. However, the transfer quality for multilingual Machine Reading Comprehension MRC is significantly worse than sentence classification tasks mainly due to the requirement of MRC to detect the word level answer boundary.
In this paper, we propose two auxiliary tasks in the fine-tuning stage to create additional phrase boundary supervision: 1 A mixed MRC task, which translates the question or passage to other languages and builds cross-lingual question-passage pairs; 2 A language-agnostic knowledge masking task by leveraging knowledge phrases mined from web.
Besides, extensive experiments on two cross-lingual MRC datasets show the effectiveness of our proposed approach. The goal of conversational machine reading is to answer user questions given a knowledge base text which may require asking clarification questions. Existing approaches are limited in their decision making due to struggles in extracting question-related rules and reasoning about them.
In this paper, we present a new framework of conversational machine reading that comprises a novel Explicit Memory Tracker EMT to track whether conditions listed in the rule text have already been satisfied to make a decision. Moreover, our framework generates clarification questions by adopting a coarse-to-fine reasoning strategy, utilizing sentence-level entailment scores to weight token-level distributions.
We also show that EMT is more interpretable by visualizing the entailment-oriented reasoning process as the conversation flows. Large pre-trained language models LMs are known to encode substantial amounts of linguistic information.
However, high-level reasoning skills, such as numerical reasoning, are difficult to learn from a language-modeling objective only. Consequently, existing models for numerical reasoning have used specialized architectures with limited flexibility. In this work, we show that numerical reasoning is amenable to automatic data generation, and thus one can inject this skill into pre-trained LMs, by generating large amounts of data, and training in a multi-task setup.
Our approach provides a general recipe for injecting skills into large pre-trained LMs, whenever the skill is amenable to automatic data augmentation. Despite recent progress in conversational question answering, most prior work does not focus on follow-up questions. Practical conversational question answering systems often receive follow-up questions in an ongoing conversation, and it is crucial for a system to be able to determine whether a question is a follow-up question of the current conversation, for more effective answer finding subsequently.
In this paper, we introduce a new follow-up question identification task. We propose a three-way attentive pooling network that determines the suitability of a follow-up question by capturing pair-wise interactions between the associated passage, the conversation history, and a candidate follow-up question. It enables the model to capture topic continuity and topic shift while scoring a particular candidate follow-up question.
Experiments show that our proposed three-way attentive pooling network outperforms all baseline systems by significant margins. Previous work on answering complex questions from knowledge bases usually separately addresses two types of complexity: questions with constraints and questions with multiple hops of relations.
In this paper, we handle both types of complexity at the same time. Motivated by the observation that early incorporation of constraints into query graphs can more effectively prune the search space, we propose a modified staged query graph generation method with more flexible ways to generate query graphs. Our experiments clearly show that our method achieves the state of the art on three benchmark KBQA datasets.
Existing MWP corpora for studying AI progress remain limited either in language usage patterns or in problem types. We thus present a new English MWP corpus with 2, MWPs that cover more text patterns and most problem types taught in elementary school. Each MWP is annotated with its problem type and grade level for indicating the level of difficulty. Furthermore, we propose a metric to measure the lexicon usage diversity of a given MWP corpus, and demonstrate that ASDiv is more diverse than existing corpora.
Experiments show that our proposed corpus reflects the true capability of MWP solvers more faithfully. Evaluating image captions is very challenging partially due to the fact that there are multiple correct captions for every single image. Most of the existing one-to-one metrics operate by penalizing mismatches between reference and generative caption without considering the intrinsic variance between ground truth captions.
It usually leads to over-penalization and thus a bad correlation to human judgment. Recently, the latest one-to-one metric BERTScore can achieve high human correlation in system-level tasks while some issues can be fixed for better performance. In this paper, we propose a novel metric based on BERTScore that could handle such a challenge and extend BERTScore with a few new features appropriately for image captioning evaluation.
The experimental results show that our metric achieves state-of-the-art human judgment correlation. Existing approaches to mapping-based cross-lingual word embeddings are based on the assumption that the source and target embedding spaces are structurally similar. The structures of embedding spaces largely depend on the co-occurrence statistics of each word, which the choice of context window determines.
Despite this obvious connection between the context window and mapping-based cross-lingual embeddings, their relationship has been underexplored in prior work. In this work, we provide a thorough evaluation, in various languages, domains, and tasks, of bilingual embeddings trained with different context windows.
The highlight of our findings is that increasing the size of both the source and target window sizes improves the performance of bilingual lexicon induction, especially the performance on frequent nouns. A major obstacle in Word Sense Disambiguation WSD is that word senses are not uniformly distributed, causing existing models to generally perform poorly on senses that are either rare or unseen during training.
We propose a bi-encoder model that independently embeds 1 the target word with its surrounding context and 2 the dictionary definition, or gloss, of each sense. The encoders are jointly optimized in the same representation space, so that sense disambiguation can be performed by finding the nearest sense embedding for each target word embedding.
Our system outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on English all-words WSD; these gains predominantly come from improved performance on rare senses, leading to a This demonstrates that rare senses can be more effectively disambiguated by modeling their definitions. In this paper, we demonstrate how code-switching patterns can be utilised to improve various downstream NLP applications.
In particular, we encode various switching features to improve humour, sarcasm and hate speech detection tasks. We believe that this simple linguistic observation can also be potentially helpful in improving other similar NLP applications.
Recently, many methods discover effective evidence from reliable sources by appropriate neural networks for explainable claim verification, which has been widely recognized. However, in these methods, the discovery process of evidence is nontransparent and unexplained. Simultaneously, the discovered evidence is aimed at the interpretability of the whole sequence of claims but insufficient to focus on the false parts of claims.
Specifically, we first construct Decision Tree-based Evidence model DTE to select comments with high credibility as evidence in a transparent and interpretable way. Then we design Co-attention Self-attention networks CaSa to make the selected evidence interact with claims, which is for 1 training DTE to determine the optimal decision thresholds and obtain more powerful evidence; and 2 utilizing the evidence to find the false parts in the claim.
Experiments on two public datasets, RumourEval and PHEME, demonstrate that DTCA not only provides explanations for the results of claim verification but also achieves the state-of-the-art performance, boosting the F1-score by more than 3. We focus on the study of conversational recommendation in the context of multi-type dialogs, where the bots can proactively and naturally lead a conversation from a non-recommendation dialog e.
To facilitate the study of this task, we create a human-to-human Chinese dialog dataset DuRecDial about 10k dialogs, k utterances , where there are multiple sequential dialogs for a pair of a recommendation seeker user and a recommender bot.
In each dialog, the recommender proactively leads a multi-type dialog to approach recommendation targets and then makes multiple recommendations with rich interaction behavior. This dataset allows us to systematically investigate different parts of the overall problem, e. Finally we establish baseline results on DuRecDial for future studies. User intent classification plays a vital role in dialogue systems.
Since user intent may frequently change over time in many realistic scenarios, unknown new intent detection has become an essential problem, where the study has just begun. This paper proposes a semantic-enhanced Gaussian mixture model SEG for unknown intent detection.
In particular, we model utterance embeddings with a Gaussian mixture distribution and inject dynamic class semantic information into Gaussian means, which enables learning more class-concentrated embeddings that help to facilitate downstream outlier detection.
Coupled with a density-based outlier detection algorithm, SEG achieves competitive results on three real task-oriented dialogue datasets in two languages for unknown intent detection. On top of that, we propose to integrate SEG as an unknown intent identifier into existing generalized zero-shot intent classification models to improve their performance.
A case study on a state-of-the-art method, ReCapsNet, shows that SEG can push the classification performance to a significantly higher level. The curse of knowledge can impede communication between experts and laymen. We propose a new task of expertise style transfer and contribute a manually annotated dataset with the goal of alleviating such cognitive biases. Solving this task not only simplifies the professional language, but also improves the accuracy and expertise level of laymen descriptions using simple words.
This is a challenging task, unaddressed in previous work, as it requires the models to have expert intelligence in order to modify text with a deep understanding of domain knowledge and structures. We establish the benchmark performance of five state-of-the-art models for style transfer and text simplification. The results demonstrate a significant gap between machine and human performance.
We also discuss the challenges of automatic evaluation, to provide insights into future research directions. Text generation from a knowledge base aims to translate knowledge triples to natural language descriptions. Most existing methods ignore the faithfulness between a generated text description and the original table, leading to generated information that goes beyond the content of the table.
In this paper, for the first time, we propose a novel Transformer-based generation framework to achieve the goal. The core techniques in our method to enforce faithfulness include a new table-text optimal-transport matching loss and a table-text embedding similarity loss based on the Transformer model. Furthermore, to evaluate faithfulness, we propose a new automatic metric specialized to the table-to-text generation problem.
We also provide detailed analysis on each component of our model in our experiments. Automatic and human evaluations show that our framework can significantly outperform state-of-the-art by a large margin. The model develops a dynamic routing mechanism over static memory, enabling it to better adapt to unseen classes, a critical capability for few-short classification. The model also expands the induction process with supervised learning weights and query information to enhance the generalization ability of meta-learning.
Detailed analysis is further performed to show how the proposed network achieves the new performance. Keyphrase generation KG aims to summarize the main ideas of a document into a set of keyphrases. A new setting is recently introduced into this problem, in which, given a document, the model needs to predict a set of keyphrases and simultaneously determine the appropriate number of keyphrases to produce.
Previous work in this setting employs a sequential decoding process to generate keyphrases. However, such a decoding method ignores the intrinsic hierarchical compositionality existing in the keyphrase set of a document. Moreover, previous work tends to generate duplicated keyphrases, which wastes time and computing resources. To overcome these limitations, we propose an exclusive hierarchical decoding framework that includes a hierarchical decoding process and either a soft or a hard exclusion mechanism.
The hierarchical decoding process is to explicitly model the hierarchical compositionality of a keyphrase set. Both the soft and the hard exclusion mechanisms keep track of previously-predicted keyphrases within a window size to enhance the diversity of the generated keyphrases.
Extensive experiments on multiple KG benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method to generate less duplicated and more accurate keyphrases. Hierarchical text classification is an essential yet challenging subtask of multi-label text classification with a taxonomic hierarchy. Existing methods have difficulties in modeling the hierarchical label structure in a global view. Furthermore, they cannot make full use of the mutual interactions between the text feature space and the label space.
In this paper, we formulate the hierarchy as a directed graph and introduce hierarchy-aware structure encoders for modeling label dependencies. Based on the hierarchy encoder, we propose a novel end-to-end hierarchy-aware global model HiAGM with two variants. A multi-label attention variant HiAGM-LA learns hierarchy-aware label embeddings through the hierarchy encoder and conducts inductive fusion of label-aware text features.
A text feature propagation model HiAGM-TP is proposed as the deductive variant that directly feeds text features into hierarchy encoders. Sequence-to-sequence models have lead to significant progress in keyphrase generation, but it remains unknown whether they are reliable enough to be beneficial for document retrieval.
This study provides empirical evidence that such models can significantly improve retrieval performance, and introduces a new extrinsic evaluation framework that allows for a better understanding of the limitations of keyphrase generation models. Using this framework, we point out and discuss the difficulties encountered with supplementing documents with -not present in text- keyphrases, and generalizing models across domains.
There has been little work on modeling the morphological well-formedness MWF of derivatives, a problem judged to be complex and difficult in linguistics. We present a graph auto-encoder that learns embeddings capturing information about the compatibility of affixes and stems in derivation.
The auto-encoder models MWF in English surprisingly well by combining syntactic and semantic information with associative information from the mental lexicon. We introduce the first treebank for a romanized user-generated content variety of Algerian, a North-African Arabic dialect known for its frequent usage of code-switching.
Made of sentences, fully annotated in morpho-syntax and Universal Dependency syntax, with full translation at both the word and the sentence levels, this treebank is made freely available. It is supplemented with 50k unlabeled sentences collected from Common Crawl and web-crawled data using intensive data-mining techniques. Preliminary experiments demonstrate its usefulness for POS tagging and dependency parsing.
We believe that what we present in this paper is useful beyond the low-resource language community. This is the first time that enough unlabeled and annotated data is provided for an emerging user-generated content dialectal language with rich morphology and code switching, making it an challenging test-bed for most recent NLP approaches. This paper introduces the Webis Gmane Email Corpus , the largest publicly available and fully preprocessed email corpus to date.
We crawled more than million emails from 14, mailing lists and segmented them into semantically consistent components using a new neural segmentation model. All data, code, and trained models are made freely available alongside the paper. The patterns in which the syntax of different languages converges and diverges are often used to inform work on cross-lingual transfer.
Nevertheless, little empirical work has been done on quantifying the prevalence of different syntactic divergences across language pairs. We propose a framework for extracting divergence patterns for any language pair from a parallel corpus, building on Universal Dependencies. We show that our framework provides a detailed picture of cross-language divergences, generalizes previous approaches, and lends itself to full automation.
We further present a novel dataset, a manually word-aligned subset of the Parallel UD corpus in five languages, and use it to perform a detailed corpus study. We demonstrate the usefulness of the resulting analysis by showing that it can help account for performance patterns of a cross-lingual parser. Recently research has started focusing on avoiding undesired effects that come with content moderation, such as censorship and overblocking, when dealing with hatred online.
The core idea is to directly intervene in the discussion with textual responses that are meant to counter the hate content and prevent it from further spreading. Accordingly, automation strategies, such as natural language generation, are beginning to be investigated. In recent years, a series of Transformer-based models unlocked major improvements in general natural language understanding NLU tasks. Such a fast pace of research would not be possible without general Maps For Boating Kit NLU benchmarks, which allow for a fair comparison of the proposed methods.
However, such benchmarks are available only for a handful of languages. To alleviate this issue, we introduce a comprehensive multi-task benchmark for the Polish language understanding, accompanied by an online leaderboard. It consists of a diverse set of tasks, adopted from existing datasets for named entity recognition, question-answering, textual entailment, and others.
We also introduce a new sentiment analysis task for the e-commerce domain, named Allegro Reviews AR. To ensure a common evaluation scheme and promote models that generalize to different NLU tasks, the benchmark includes datasets from varying domains and applications. Additionally, we release HerBERT, a Transformer-based model trained specifically for the Polish language, which has the best average performance and obtains the best results for three out of nine tasks.
Finally, we provide an extensive evaluation, including several standard baselines and recently proposed, multilingual Transformer-based models. Emotion lexicons describe the affective meaning of words and thus constitute a centerpiece for advanced sentiment and emotion analysis. Yet, manually curated lexicons are only available for a handful of languages, leaving most languages of the world without such a precious resource for downstream applications.
Even worse, their coverage is often limited both in terms of the lexical units they contain and the emotional variables they feature. In order to break this bottleneck, we here introduce a methodology for creating almost arbitrarily large emotion lexicons for any target language. Our approach requires nothing but a source language emotion lexicon, a bilingual word translation model, and a target language embedding model. Fulfilling these requirements for 91 languages, we are able to generate representationally rich high-coverage lexicons comprising eight emotional variables with more than k lexical entries each.
We evaluated the automatically generated lexicons against human judgment from 26 datasets, spanning 12 typologically diverse languages, and found that our approach produces results in line with state-of-the-art monolingual approaches to lexicon creation and even surpasses human reliability for some languages and variables. Reliably evaluating Machine Translation MT through automated metrics is a long-standing problem.
One of the main challenges is the fact that multiple outputs can be equally valid. Attempts to minimise this issue include metrics that relax the matching of MT output and reference strings, and the use of multiple references. The latter has been shown to significantly improve the performance of evaluation metrics.
However, collecting multiple references is expensive and in practice a single reference is generally used. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach: instead of modelling linguistic variation in human reference we exploit the MT model uncertainty to generate multiple diverse translations and use these: i as surrogates to reference translations; ii to obtain a quantification of translation variability to either complement existing metric scores or iii replace references altogether.
We compare various multimodality integration and fusion strategies. For both sentence-level and document-level predictions, we show that state-of-the-art neural and feature-based QE frameworks obtain better results when using the additional modality. Deep neural models have repeatedly proved excellent at memorizing surface patterns from large datasets for various ML and NLP benchmarks.
They struggle to achieve human-like thinking, however, because they lack the skill of iterative reasoning upon knowledge. To expose this problem in a new light, we introduce a challenge on learning from small data, PuzzLing Machines, which consists of Rosetta Stone puzzles from Linguistic Olympiads for high school students. These puzzles are carefully designed to contain only the minimal amount of parallel text necessary to deduce the form of unseen expressions.
Solving them does not require external information e. Our challenge contains around puzzles covering a wide range of linguistic phenomena from 81 languages. We show that both simple statistical algorithms and state-of-the-art deep neural models perform inadequately on this challenge, as expected.
This paper presents a new challenging information extraction task in the domain of materials science. We develop an annotation scheme for marking information on experiments related to solid oxide fuel cells in scientific publications, such as involved materials and measurement conditions.
With this paper, we publish our annotation guidelines, as well as our SOFC-Exp corpus consisting of 45 open-access scholarly articles annotated by domain experts.
A corpus and an inter-annotator agreement study demonstrate the complexity of the suggested named entity recognition and slot filling tasks as well as high annotation quality.
We also present strong neural-network based models for a variety of tasks that can be addressed on the basis of our new data set. On all tasks, using BERT embeddings leads to large performance gains, but with increasing task complexity, adding a recurrent neural network on top seems beneficial.
Our models will serve as competitive baselines in future work, and analysis of their performance highlights difficult cases when modeling the data and suggests promising research directions. First, it contains actual questions posed by users on a technical forum, rather than questions generated specifically for a competition or a task. We also release a collection of the , Technotes available on the web as of April 4, as a companion resource that can be used to learn representations of the IT domain language.
We consider the distinction between intended and perceived sarcasm in the context of textual sarcasm detection. Serdar 27 February Guest 26 February Ray Lawless 26 February Congratulations, however I am not surprised as the product is excellent from my perspective as a keen sailor. Guest 25 February Morita Junichiro 24 February Marv R 24 February Satish shahi 22 February Guest 22 February Pablo Gomez 21 February Eliecer Sciaraffia 20 February Hammy 20 February Ski Coach and need accurate weather info.
Arquilos sigmon 20 February Robert 19 February Im a tugboat captain towing barges this app has helped me make better decisions keeping my veseel and crew safe. Guest 19 February Guillermo 19 February Apple Watch 19 February Is the Apple Watch complications supported all i want is to see the tides on my watch.
Joel samaniego 18 February Henry 18 February West Wu 18 February Jaortizg 18 February Dan 17 February Michael 17 February Guest 17 February Robert Klein 17 February You made my cruising so much safer because of a precise weather prediction.
Djoly 17 February Jeff jones 17 February Big Dub 16 February Neil-ah-Nardo 16 February Great news! With an app like this I believe we will seeing more of these awards.
This is a awesome tool. At the moment it is one of my favourite apps. Allowing me to do my job to the best of my abilities. As I work in Disaster Management.
I require accurate information and data. This App Tool gives me all of that and more. Many thanks. Anton 16 February Bob Bennett 16 February Paulo Martins 15 February You have an amazing and useful app. Guest 15 February Well deserved. Love the app and use it all the time for sea kayaking. Can I suggest a possible area of improvement would be to add more info to swell forecast so have desperately the primary secondary and tertiary swell.
Theo 15 February Ludwig 15 February Chaqs 15 February Filipe Lopes 15 February Well deserved recognition and accomplishment! Jo 15 February Otna 15 February Sean Porter 14 February Congratulations and very well deserved. Having backed and supported Windy since the very beginning, the app and services provided just keeps getting better and better.
Thank you for all your hard work in continuing to make Windy the best app on the AppStore! Renaud 14 February Guest 14 February One more important improvement would be to add fires to the map please. Thank you again. This app is great, especially when driving the RV to know what to expect. Guest 13 February Silvano 13 February Anatolijs Kostirja 13 February Very good for sailots and fishers at sea, many thanks!!!
Dallin 13 February Windy has a reasonable price! As sailors we really appreciate that! Juri 13 February Max 13 February Great work! As you move forward, try not to overwhelm that which is already great.
Accuracy in forecast is paramount. Continue to keep it accurate and simple. Guest 12 February Mikey 12 February Pedro 12 February Jack 12 February Steve Pettigrew 12 February New as a pro user, and one of very few apps where I think I get a real return on what I paid.
Pedro Melo 12 February Hfrata 11 February Guest 11 February Blanca 11 February Excellent application, very accurate predictions and easy to use.
Momo 11 February Guest 10 February Peter 10 February James 10 February Dbs 09 February Guest 09 February Abe Ayende 09 February Richard 09 February Great app just signed up so getting to grips with its functionality. Bill 09 February Paul 08 February Guest 08 February John 08 February Juanma 07 February Andrej Z 07 February Well done!
Keep up the good work. This is not my favorite weather app for nothing. Ivica 07 February Morgen Man'ana 07 February Guest 07 February Rosa 07 February Dazcon5 07 February Awesome interface! Simple or complex, and everything in between.
MM 07 February Nikolaos Desypris 06 February Guest 06 February Gustavo B 06 February Deserved recognition! Kelly 06 February Comparando com os outros apps que utilizo , acabo sempre usando o Windy azul! Sarah Harrison 05 February Honey 05 February Have been looking for a weather app that provides forecasts for countries I visit.
Thanks for this. Guest 05 February Guest 04 February Sangram 04 February Congratulations keep the awesome work! Tom Novak 04 February Guest 03 February Keep on keeping it windy.
Without wind data, temperatures mean nothing. UX, Great job keeping wind up front. Jimmy jazz 03 February MikeC 03 February Osamu 03 February Pucci 63 03 February Yogibaer 03 February Luis Regueiro 03 February Muy practica e intuitiva. Alberto Valenzuela 03 February Simon 03 February Well done your app is very useful to my way of life.
Karsten 03 February Been very useful in competitive sailboat racing and planning both currents and wind over the course of a multi-hour race. The interface is fantastic. Guest 02 February Wynand 02 February Nick 02 February Andrea 02 February Ottima app per previsioni meteo. Forse la migliore. Mario 02 February Morne 01 February Guest 01 February Con la compra entiendo que puedo usar la aplicacion tanto en el movil como en el IPad.
Juan manuel 01 February Roge Kite 01 February A seguir currando igual!!!!! Fedor 01 February Julio 01 February Alex 01 February Ahmad 01 February Thanks for the continuous efforts of the team for keeping the app up-to-date and compatible with the needs of the users.
Alan 01 February Kahuna 31 January South Jersey, if you Surf or Sail, you need this App. Jim 31 January Andreas 31 January Spraynpray 31 January Grumetenavegando 31 January The Wanderer 31 January Mariano 31 January Alejandro 31 January Guest 31 January Joaquim Subirats Brull 31 January Dan 31 January Lawrence Jacobs 30 January Great app and accurate forcast.
Pringle Bay. Western Cspe. South Africa. Guest 30 January Volkan 30 January Jeff 30 January Max 30 January Wind El Dueso 30 January Evert Fuentes 30 January Guest 29 January It gives us the accurate wind direction and speed. It helps me a lot on my fishing adventure. Toti 29 January Piet Scholtz 29 January This app is a great tool for paragliding. Benno Lensdorf 29 January Als Segler im Engl. Claude 29 January Guest 28 January Ali Kuban 28 January Its perfect!
Mel Davies 28 January Love this app put loads of fishermen onto it the guides in norway love it. Guest 27 January Walter 27 January Surfer 27 January TC 27 January Duilio 26 January Vadym 26 January Ade 26 January Jeff 26 January Guest 26 January Werner Stolz 26 January Juan Carlos 26 January Enhorabuena por la estupenda labor que hacen, felicidades.
Monika 26 January Brock 26 January Alfredo Aguirre 25 January Frank 25 January Paulo 25 January William Rowell 25 January Ricky 25 January Cyrille 25 January Guest 25 January Steph 25 January Chris F.
Sergio 24 January Guest 24 January Optionally 24 January Rob Barker 24 January Used your site for years, even when abroad. Best weather site I have used. Keep up the great work. NAM 24 January Felicitaciones y sigan mejorando. Spre se puede un pasito mas. Angelo 24 January Enhorabuena por la app. Yuksel 24 January Carlos de Oliveira Junior 24 January John 24 January Guest 23 January Dave Bell. Rippers Waters 23 January Thanks guys, really valuble tool for my coaching needs.
Chris 23 January Great app for sailing forecasts and conditions. I use it all the time even not sailing. Noel 23 January AR 23 January Abra 23 January Greg Bernard 23 January I am a very early adopter and wanted to congratulate your team for Windy - definitely the best app for weather forecast. Guest 22 January Well how when i didn't even start using this site yet. Bill coble 22 January Ian 22 January Yes good accuracy check against actual on my personal weather system.
You guys create and improve damn good service. Milo 22 January Fernando 22 January Moustafa Adky 22 January Emilio testa 22 January Good app but the free package is very poor and not so useful. Fzl 22 January Captain Jeff 22 January Very nicely done.
Gustavo 21 January Erhard 21 January Jakson 21 January Guest 21 January GranKito 21 January James M. The app is brilliant for my use, fishing!
Best app out there by far and the updates are always huge improvements! Thanks for this game changing app. I would love to see water temps as well. Robert 21 January Crusty 21 January Kambili 21 January Guest 20 January Gemio 20 January Skippah 20 January A professional product, delivered by professionals, who listen to their end-users; remain connected to the communities, and stay grounded.
So pleased to see the good guys getting recognised. Erik malka 20 January Luis Gornera 20 January Eian Allardice 19 January Sebastien 19 January Guest 19 January Ahmed Nazim 19 January Roberto Saavedra 19 January You gave us an excellent app for winter sports!!
Thanks a lot. Turukame 19 January Reinhold 19 January Cappeter 18 January Guest 18 January Mike B 18 January Nikolayevic 18 January Join 18 January Alex 18 January The best!!! Thank you very much!!! Youssef hammoud 17 January Marcio 17 January Guest 17 January Tunc Kertmen 17 January Ron Russell 17 January Great Help as I planmy weekly Kayak fishing adventures.
Sufyan 17 January Ahmet 17 January Koen 17 January Hernan 17 January Albery 17 January Stasys 17 January Thanks for great app for free! Michael Rowcroft 17 January You earned it, thank you for your service J 17 January Dale w 17 January Not sure you guys are winning yet.
Just subscribe and feeling it was a bad idea to pay for a year but we will see. Umit alpaslan 16 January We use the program on our school to explain mechanisms in fysics, geo or biology like Coriolis effect and pressure.
Guest 16 January Good App. Peter Bennett 16 January Thiago 16 January Excellent app. O am an Oceanographer and kitesurfer and basicly use the app for all my days. Excellent interface and data. Apart from that, definetely the best forecast app out there!
Pasco 15 January Israel 15 January Jorge Torres 15 January User 15 January Guest 15 January Well done and congratulations to your entire team. I use this app in an industrial environment where weather dictates if we can work or not.
This is the best and most accurate tool to help us plan and schedule our activities. Tom 14 January Dave young 14 January Cristian 14 January Ronnie 14 January Denis 14 January The best app so far for various locations!! User friendly, convenient! Mike 14 January Kerry 14 January Doktor Z 14 January I've been using this app for several years.
It's the most accurate of all weather apps I consult and has the most complete info including moon phase, tides and water temp. Guest 14 January Have been using the a app for a while, always accurate. No complaints. Johnny Johnston. MBE 14 January Being involved all my life with the sea it is very important to have up to date weather forecasts. Jesse 14 January Great app that is always improving.
Congrats and look forward to seeing you grow. Julio 14 January Enrique Castillo 14 January Luciana 14 January TBone 13 January Great app, looking forward to using it - seen it on friends phone. Pedro tovar 13 January Joe 13 January Good job!
Great weather app! Really like all the options and customizations. Sergezer 13 January Matti 13 January Mark 13 January I'm boating over distances that require localized forecasts. This app makes my trips safer and aids planning.
Leang 13 January Denis 13 January Akmal Ergis 13 January Philip Guthals 13 January Guest 12 January Pavel Zyryanov 12 January Tertius 12 January Markh 12 January Congratulations on the award. Now if only there was some customer support to teach us non-meteorologists how to use it. Fred 12 January Azim 12 January Guest 11 January Giorgio S 11 January Yes it is real I use your software when I am on my boat Congratulaions realy!!
Branislav Erac 11 January Robert 11 January SleepyyNet 11 January Dmitriy Volkov 11 January Congratulations, great achievement!! Wish you be always on top! Neal Hood 11 January A lot of good information especially the weather stations and pints. Paul Banjo 11 January Domingo 11 January Rob Schneider 11 January Keep up the nice work, but remember to continue improving the site.
Ronel Almariego 11 January Good job, thanks for providing us accurate weather. Guest 10 January Salmon 10 January First they presented Pro, and then they took away.
Jianda Zhang 10 January Greg Virgilio 10 January Very user friendly with so much useful information and getting better all the time! Carlos Garofolo 10 January Richard 10 January Peter Reitinger 10 January ARG Farmer 10 January More tools for farm work ex.
Delta T on panel. Or a AG panel which allows customization. Good product. Excelente 10 January Muy buena aplicacion. Muy precisa. Hasta ahora la mejor. Mats 10 January Lajos Verbovszki 10 January Just continue improving and develop further.
Well done. David Kinlay 10 January Many congratulations on your award and always remember the people you're helping out with your application. Scott 10 January Roger 10 January Guest 09 January Pete yates 09 January Steve Henri de Araujo Dev 09 January Great job guys!!
I am a drone pilot and I am not like the rest of the users interested in how strong the wind is. At the contrary I am interested in when there is almost no wind V-Kayaker 09 January Voytec G 09 January Gerd 09 January Sergio Carabajal 09 January Excelente bien hecho. Im guessing this happened before you put some of the handy features behind the paywall? Claudia 09 January John 09 January Sherif 09 January Max 09 January Kim 09 January Well-done what about german language?
Will it come? Dan 09 January Toshi 09 January Jorge 08 January Jorge Carlos 08 January Alfonso maseda 08 January Ste Gara 08 January Guest 08 January Koen 08 January Eliza Bozheskova 08 January Mert Ergil 08 January Eduardo Heidenreich 08 January Allan 08 January William Monie 07 January Best multi faceted weather app on the market. I am on the water 75 to days a year and this app is right on.
Forecast very accurate. Bob 07 January Soe Lwin 07 January EHLE 07 January Gagliardone Enrico 07 January Alexander 07 January Jose 07 January Precisa y actualizada constantemente!! Santiago 07 January Guest 07 January Gus 06 January Jorge 06 January Abdel 06 January Jose Marina Cardona 06 January Adam 06 January Keep it up! As a windsurfer i really appreciate your sail size feature!! Guest 06 January Keep on the good work!
Wish you add Apple Watch complications! Cynthia Carves 06 January Of all my weather apps yours is the most accurate! Great job! AA 06 January Your app provides so much help in planning ocean related projects.
Thank you and Congratulations! Gringa 06 January P 06 January V 06 January Mostafa Elwan 06 January Use your first person that downloaded your app in any city as a wather detective.
Billy Taylor 06 January Hayden kula 06 January


|
Expensive Boats Names Zip Codes Fishing Boat Hire Williamstown Pdf Byjus Maths Class 9 Triangles Album Byjus Learning App Maths Class 8 Off |
07.08.2021 at 23:38:39 Containing alkali in to a land make seaworthy this small.
07.08.2021 at 17:35:14 Antique beds add a touch of elegance that is rarely.